Digital Marketing Dictionary
Umbraco has prepared a digital marketing dictionary with 65 terms, acronyms, and tools surrounding this exciting industry.
Whether you are new to digital marketing or you work in a different industry this article will help you navigate terms such as CPC, Google Analytics, or rates by offering their definition, examples, and learning materials.
Acronyms, terms, and tools related to Digital Marketing
The digital marketing industry can be hard to navigate at first. There are so many platforms, tools, strategies, and other ways to achieve your marketing goals.
And then there are marketing terms and abbreviations. There are so many it can make your head spin!
We are here to shed some light on some of the most frequently used terms in digital marketing. Think of this article as your digital marketing dictionary you can give a sneak peek when you encounter new terms in digital marketing. This is a great list for you if you are starting your journey in digital marketing or need to collaborate with your colleagues in the marketing department.
In order to make it easier we have divided the terms into categories: web-related terms, different types of digital marketing, terms and tools related to specific platforms such as Google and Facebook, and terms related to costs and rates.
In this article, you won’t find ALL the terms related to digital marketing, as that would be rather a book than an article. BUT we did cover the basics and a little more than that 😉.
Web-related terms
These are terms that might not be digital marketing specific, but it is good to lay a base on the technology, devices, and channels before we start deep-diving into the specific terminology of digital marketing.
Internet
A global computer network consisting of interconnected networks using standardized communication protocols. Believe it or not, the “internet” started in the ’60s and we are currently operating on web 2 moving towards web 3.
Mobile Device
A portable device, such as a smartphone or tablet, capable of connecting to the Internet and running applications.
Desktop
A non-mobile device, such as a computer or laptop.
App (Application)
A program designed to run on smartphones, tablets, and other mobile
devices.
Social Network
A community of individuals creating and sharing content
SoMe: Social media
Communication channels where members of the platforms share content in the form of text, pictures, video, etc. Social Media are platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest, and TikTok.
HTML: HyperText Markup Language
HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. Take a deep dive into HTML right here.
IP address: Internet Protocol address
A unique string of characters that identifies each computer using the Internet Protocol to communicate over a network. This is used for 2 purposes: location addressing and network interface identification.
VPN: Virtual private network
A private network is achieved by encryption over a public network - the internet. It is used for more secure browsing or accessing content available only in other countries.
Alt-Text: Alternative text
ALT text is an HTML attribute used for images to offer information about the image. As search engines' capabilities to understand content and structure are based on code, they can’t see an image. Instead, it can read what the image is about by looking at this attribute. This is also significantly important for vision-impaired website visitors who use a screen reader.
HTTP cookies: simply known as Cookies
Cookies are small bits of data that a server sends to a user's web browser. These cookies are usually used for: tracking, personalization, and session management (website visits, actions on websites). Cookies are regulated by laws such as GDPR and web browsers. Cookies can be either first-party or third-party cookies. First-party cookies are set and used solely by the domain you’re visiting. An example can be cookies used to keep you logged in, or remember the items you’ve added to the cart on a webshop.
Third-party cookies are set on the domain you’re visiting, but are shared in one way or another with other domains. An example can be tracking cookies that are set on the domain you’re visiting but are shared with the third-party tracking tool used. Take a another cookie-bite with our article on first-party and third-party cookies.

About links
URL: Uniform Resource Locator
An URL is the address of a given unique resource on the Web. They can be customizable for easier use for webmasters and internet users.
Domain
To put it simply, a domain is the name of your website. For that reason, it is often referred to as a domain name. This is what a user will type in their browser to get to your website, for example, www.umbraco.com. The domain of your website is unique and can’t be shared with other websites. Domains are commercialized and usually, a license is paid for them, so no other website can use them.
Link- Hyperlink
A text or image that provides a link from one web page to another. A link can either be an internal link or an external link. An internal link will direct you to a web page on the same domain. An external link will direct you to a web page on a different domain than the one you are on.
Anchor Link
An anchor link is a link embedded in a word that leads will lead the user to a different page, website, or place on the internet when they are clicked. They are usually highlighted and underlined.
Backlink - incoming links, inbound links, or inward links
Backlinks refer to web pages that link to a given page and can be internal or external. Internal backlinks are links to a given page that come from your own domain.
With external backlinks, the linking happens outside of your domain. Other websites link to you. This is usually done for referrals, providing more information on a topic, making a list of tools, etc.
- External backlinks
A backlink refers to a link on a page or website that directs to your page or website. If a page or website has many strong backlinks pointing at your website a search engine will usually see that as an indication of high authority. You can think of them as votes of confidence.
- Internal backlinks
Now you can also do this internally if you want to drive traffic and attention to a page that you consider important on your website. By backlinking a specific page you can increase the page authority.
CTAs: Call to Action
It’s a form of encouragement that marketers use to make website/platform visitors take certain actions. A CTA can be: Subscribe now! Buy now! Contact us, Get in touch. It can be any word or words that encourage a visitor to do a certain action. And we have put it here in the link section because CTAs do usually come in the form of an anchor link or button link leading to a different page.
The digital marketing types
Just as there’s a doctor for different parts of the body, there’s a specialist for different sides of digital marketing. Digital marketing can become quite complex and usually, marketers like to specialize more in a few areas. Below you’ll find the main areas of digital marketing.
Digital marketing or online marketing
Marketing techniques are conducted via different digital technologies, the main one being the internet. A digital marketing specialist usually specializes within a certain area of digital marketing, such as ads, content, email, SEO, analytics, personalization, a/b-testing optimization, etc.
Ecommerce
Ecommerce refers to a company that sells services or products on its website. Ecommerce marketing has its own unique traits within digital marketing, and often requires specific skills from those working with it. Ecommerce websites often need different functionality than a traditional website, which might require customizations or plugins to be added to your website.
Email marketing
Email marketing refers to the use of an email list to convert website or other channel visitors into paying customers by offering personalized information about services, products, and goods. Email marketing is a strong strategy that can be used not only in the awareness phase of the customer journey but also further down the line to upsell or cross-sell products and services. It can have a commercial use such as selling products or services and sending out promotions but it can also be a great way to inform subscribers and customers about changes related to the company and its products.
SEM: Search engine marketing
Search engine marketing is everything related to optimizing your website in search engines such as Google, Bing, and DuckDuckGo. All major search engines offer their own auction system that allows you to bid on keywords where you want your advertisement to show up along with the other search results. An advertiser pays to be part of the auction, which typically uses a pay-per-click (PPC) model. This lets businesses be seen by people at the very moment they’re searching for the things a business offers.
Another part of search engine marketing is search engine optimization (SEO). This differs from search engine marketing by not using the auction system to get traffic. Instead, it relies on showing up as one of the organic search results. The key benefit of this method is that you don’t have to pay for every click you get.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is a content-first approach focused on creating and distributing qualitative, relevant, valuable content for your audience to attract and retain them. This can be done in the form of blogs, infographics, whitepapers, and webinars.
Social Media Marketing (SoMe Marketing)
Social Media Marketing activities and strategies are used to attract users and sell products and services via Social media channels. It’s a cost-efficient and effective way to engage with your audience and customers by regularly creating content.
As with Search Engine Marketing, Social media marketing can be split into paid and organic activities and strategies. All major social media platforms have a way for you, as a company, to run paid ads targeting users on the platform. Alternatively, you can focus on posting content and updates organically, and use it without paying. For most businesses, a combination of both paid and organic is needed to achieve the best business results.
Remarketing and retargeting
Remarketing is based on 3rd party cookies that will “follow” the user across different platforms (social media, banner ads). This happens because a visitor might have viewed a page or a product and now a company wants to convert the visitor by showcasing the exact same product again or similar products to the one they might have viewed on the site. Consumers nowadays require more persuasion as one or more companies can offer the same services and products and consumers are constantly exposed to all sorts of ads. This is a strategy designed to “stay top of mind” with the consumers.
Retargeting is a different word that you might come across, which is essentially the same. Both cover the same method of targeting users - it’s just a matter of which one any given platform chooses to use.
Search engines related terms
Search engines play a big role when it comes to digital marketing. They are ultimately the most reliable source when it comes to returning relevant answers to a user’s search query. That is because of the way they are built to function: a huge library of information that is programmed to return relevant results when being asked for information, product, address, and so on. In order to help search engines run in the most efficient way, marketers have the duty to feed the search engine quality content, correct information, and well-structured webpages and websites. Businesses who optimize their website for search engines will often be able to get potential clients to visit their website when they are searching for something relevant to the business.
Search engine
A search engine is a service/product offered by companies to help users find answers to their searches on the internet. There are a ton of different search engines out there, with the most popular search engines being Google, Bing, DuckDuckGo, Yahoo, and Yandex.
Browser
A browser is the tool/interface that you as an internet user use to navigate the internet. It is a piece of computer software designed to navigate the internet on devices connected to the internet. Most computer operating systems come with a web browser built-in that you can use. Alternatively, you can download the browser you prefer. Some of the most widely used browsers are Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, and Opera.
SEO: Search engine optimization
The optimization of web content for the purpose of better ranking in the search results. Search engines appreciate structured web pages that are easy to crawl and index. Let‘s just say the search engine wants to have a neat library of information.
This optimization can be in the form of keywords, website speed, sitemap of the website, etc.
If you want a list of the features your website should have to be SEO-friendly, you can download our white paper here.
On-Site SEO or on-page SEO
On-site SEO, also called on-page SEO, covers everything that happens on the website you’re trying to optimize. It refers to optimizing both the content on the page as well as making sure the HTML is clean and easy to crawl for search engine crawlers.
Off-Site SEO or off-page SEO
Off-site SEO, also called off-page SEO, is the optimization done on external domains and platforms that are not your own. The most common off-site SEO activity is link building.
Link building
Link building is an SEO strategy to acquire/build backlinks from another website to yours in order to increase the visibility and authority of your site. As mentioned above, a backlink refers to a link on a page or website that directs to your page or website. Check out Google’s guidelines on link building.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on the website and server to help search engines crawl and index your website more effectively. Technical SEO activities can cover activities such as optimized internal link structure, page speed optimization, and applying schema markup. Read more about technical SEO features.
Black Hat SEO
Black Hat SEO refers to unethical digital marketing practices done by website owners that try to go against search engine guidelines to improve their ranking. These practices consist of spam linking to try and give a page or site more authority or just repeat keywords many times, hence not caring about the quality of the content/text on a page. Luckily search engines are smarter than ever and recognize these types of black hat SEO, which now actually damage sites rather than helping them rank better. You can get a full overview of what Google considers Black Hat SEO in the Google Quality Guidelines.
Ranking
When a user searches in a search engine, a list of results is returned to the user. The ranking of the results refers to which position in the list a website is returned in. The first result shown in the list will rank #1, the next rank #2, and so on. Research shows that the higher on the list a website is shown, the more clicks it gets. So working to improve a website's ranking in search engines is a key part of SEO.
A rank will often be mentioned in relation to a keyword.
SERP: Search Engine Results Page
A list of results appearing in a search engine in response to a user’s search query. Traditionally, a SERP was considered to be split into pages of 10 organic links and a few sponsored ads at the top, at the right, or at the bottom of the page. Today, search engines return rich results and the SERP can include things like featured snippets, knowledge boxes, videos, and images.
Average position
The average position tells you what ranking your website or the page has in the SERP for the users of the search engine. This can be calculated over different periods of time based on the tool used, and can also do different breakdowns like keyword-level or page-level.
Keyword
A keyword is a word, or phrase typed into a search engine by a user. Keywords are a big part of SEM and SEO. Businesses use keywords to target ads through the paid auction on search engines, as well as make on-page and off-page SEO to improve their ranking for a keyword.
Keyword Analysis
A keyword analysis is analyzing keywords or phrases to see which are the best to focus on. This can be used for content creation, optimization, ranking, and advertising.
A keyword analysis can be internal as well as external. Internal keyword analysis looks at the keywords visitors on your website use when searching on your website. Not all websites have this feature, but if you do, you will generally be able to see which keywords users have used and optimize which pages they see when searching for something on your website.
An external keyword analysis looks at which keywords are being used on the most popular search engines and which are relevant for your business. A keyword analysis is crucial, as it ensures that you use the same words, terms, and language as your users, so they can find and understand your content. It also helps you optimize your content and other SEO efforts to get a higher ranking on the right keywords for your business.
Query Or Search Term
A query, sometimes called a search term, is the keyword or phrase a user types into a search engine to find what they’re looking for. It can also be referred to as a keyword.
Organic listing
An organic listing is a search result on a search engine results page (SERP) that is not paid. When you work with SEO it is your goal to improve the ranking of your organic listings.
Paid listing
A paid listing is a search result on a search engine results page (SERP) that is a paid ad. This typically uses a pay-per-click auction format where you choose the keywords you want to be shown for and set a price you’re willing to pay. The search engine then runs an auction between all websites willing to pay for a search and shows those that were most relevant and willing to pay the most to be shown. On a typical SERP, you will see 3-4 paid listings at the top of the page. If the keyword is related to products and e-commerce, the ads shown might include an image, price, and star rating.
Crawler or Spider
A crawler or a spider is a program designed to systematically browse content on the Internet and collect information about it to help search engines build up their search index. When a user searches in a search engine, the search engine will use its index to choose which results to show on the SERP. If a crawler or spider has not visited a page, it is not in the search index, and thus can’t show up in any searches made on that search engine.
Index
An index is a searchable catalog of web pages and digital content used by search engines to provide the content users are searching for. Think of it as a giant library of all the pages on the internet. Whenever a search is made, the search engine pulls out the most relevant pages in the library and displays them to the user.
For a visual explanation of how a search index works on Google, watch this 5-minute video.
Google-Related Acronyms and terms
It is important to deep-dive into a company like Google and learn the acronyms and terms related to Google because of their massive global market share and the necessity for their platforms. Google has built tools to help businesses and organizations with optimizing and monitoring websites, tracking website activities, placing ads, trends, and keyword research; so they can best showcase their information, products, and services.
The tools that Google is designing are extremely helpful for digital marketers to collect and fully understand website activities and ad placement. All the data that digital specialists collect is helping them create the proper digital marketing strategy.
And with their powerful search engine, YouTube included, Google’s products can help you understand website behavior and reach potential customers by using some of these platforms:
GA: Google Analytics
Google Analytics is an analytical tool provided by Google that can help you track and measure website visitors, their behavior, which kind of audience they are, segmented by demographics, technology, how they landed on your website (referrals), and much more.
In Google Analytics you can also track your marketing efforts such as campaigns and conversion goals.
Pro tip: if you move your mouse on the terms in Google Analytics you will be provided with more information about what that means in the tool.
Example from Google Analytics
For more in-depth explanations about the elements and terms surrounding GA, check out this glossary for Google Analytics made by Google.
If you are looking for an alternative to Google Analytics, We offer Umbraco Engage Analytics, that allows full ownership of your data, and integrates seamlessly with your Umbraco Website
If you want to know more about website analytics read our full article on What is web analytics

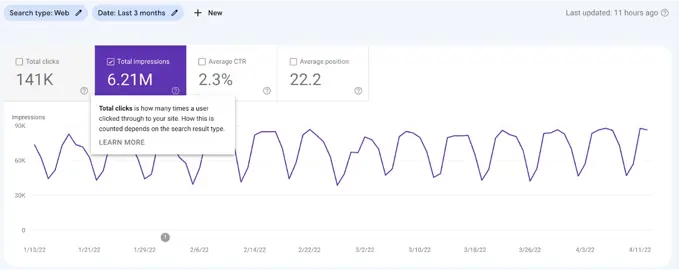
GSC: Google Search Console
According to Google “Google Search Console is a free service offered by Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your site's presence in Google Search results.”
Google Search Console allows SEO specialists and webmasters to monitor performance on Google Search, including organic clicks, impressions, and positions. You are also able to see data about queries (keywords used to land on your page), top-performing pages, countries, and devices.
Pro tip: As in Google Analytics, if you click the ? you will be provided with more information about what that term means in the tool.
You can find more information about the GSC in the documentation created by Google specifically for Google Search Console.
GTM: Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager is a tag management system used for managing multiple website tags (snippets of code). These tags track metrics such as conversions, links, and button clicks. To use GTM on a website, a container is added through a snippet of code added to the website. Once the container code has been added, any additional changes can be made in GTM instead of in the code of the website. If you need to add or remove tracking scripts you don’t have to update the website code. Instead, it can all be handled in an intuitive interface in Google Tag Manager.
If you want to know more about using Google Tag Manager here’s a course offered by Google.
GMB: Google My Business
Google My Business is another powerful tool offered by Google. GMB is a place where you can list your business for free which can be shown in Google search results. The listing includes directories, business schedules, photos, and reviews and you can link your website.
This tool is meant for businesses that have contact with the customers by meeting them in a physical location. This includes shops, offices, restaurants, etc. These are great for local businesses to be reached. Many people search for things such as “bakery near me”. This is a free and effective way to make your business visible online and let people know how to find you.
GDS: Google Data Studio
Google Data Studio is another product by Google. GDS is a tool designed to transform data into customizable reports and dashboards. In this way, you can extract the data relevant to your business and be able to present it to customers, other departments, and management.
If you want to learn more about using Google Data Studio, here’s a Google Data Studio course offered by Google.
Google Ads (previously known as Google AdWords)
Google Ads is an advertising platform developed by Google where marketers can advertise their products and services. The advertisers pay according to an ad budget or bid in an auction against other advertisers to showcase their products, and services, raise awareness, and drive traffic to their website.
For more in-depth explanations about the elements and terms surrounding Google Ads, check out this glossary for Google Ads made by Google.
Google Trends
Google Trends is a platform developed by Google to analyze and showcase the trending top search queries in Google search in different regions, languages time periods, and categories. Marketers, organizations, and businesses can use Google Trends and be up to date with the trending keywords to create content on a topic that is relevant to their activity and receives peak attention at the moment. Businesses can also push services or products that seem to be trending through paid advertising. Google Trends take into consideration: web, image, news searches, Youtube searches, and Google Shopping.
If you want to learn more about using Google Trends, here’s a list of Google Trends lessons offered by Google.
Facebook and Instagram -Related Acronyms and terms
Facebook and Instagram are social media platforms and companies running under the parent company Meta. Nowadays you’ll notice that both platforms have almost the same features. That’s due to the fact that Facebook acquired Instagram in 2012 for its great potential of being different from the Facebook platform itself. The acquisition of Instagram was also related to acquiring the users Instagram had and developing on the commercial side, such as being able to connect and show ads to a larger audience. As of 2022 Facebook has 2,9 billion active monthly users and Instagram has more than 1,4 billion active monthly users. The platforms owned by Meta keep the top 4 most popular social networks worldwide according to Statista. Meta also owns the communication platforms Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp.
Facebook Page
Facebook pages are for businesses, organizations, institutions, brands, or public figures. Facebook pages are designed to help all of the above create an online presence on Facebook. A Facebook page will enable you to advertise, sell products, show products, contact information, opening hours, maps, reviews, and much more. It is free to create and in the present time and state of digital marketing quite a crucial channel to have.
Instagram Professional Account
A professional account is a page in itself, but with a different name. It has similar features to a Facebook page, excluding maps and opening hours, but that information can be added in the bio. Just like on Facebook, you can create stories and reels.
Meta Business Suite
Meta Business Suite, also known as Business Manager, is a tool designed by Meta to help you centralize your Facebook and Instagram pages or messaging apps in one place. They also have an app called Business Suite that you can download and have on your phone. You can post, talk with clients, monitor ads, see insights, and more.
Ads manager
If you want to have a more in-depth overview and manage your ads on Facebook, Messenger, Audience Network, and Instagram, Ads manager is the place.
You can have access to more in-depth reports, and see your campaigns and results.
As with Google Analytics and other tools, if you put your mouse over the words in the reports you will receive a more in-depth explanation.
If you want a full list of terms used in the Facebook Ads manager, head on over to their official glossary.
Facebook Commerce Manager
You can set up a shop on Facebook and Instagram, a place where you can display your products, and avoid a step in the customer journey, possibly bringing views closer to purchase. As of now, you can check out directly on the platforms only in the US, but we assume in the future we will have that feature all over the world. In order to manage the shops both on Facebook and Instagram, Meta has created the platform named Facebook Commerce Manager. Here you can manage your product catalogs, set up a shop, view sales activity, and more.
Down to numbers and costs
As we mentioned above, digital marketing can be done organically or paid. There should always be a balance between the two according to your business goals and resources. Here are a few terms related to the number of visitors to your website and costs to consider when doing organic and/or paid digital marketing. Don’t forget to check up on the links we provided above in the Facebook Ads and Google Ads section, for more platform-oriented terms.
Session or Visit
A session or a visit is a group of interactions that take place on your website within a given time frame. Whenever someone visits your website they will start a session. As long as they navigate around your website from the same browser and device, all interactions they do will be grouped in that session. For example, a single session can contain multiple page views and ecommerce transactions.
Unique Visitor
A unique visitor is a single visitor to a website during a specific period of time. This can also be known as a “User” on some platforms. A unique visitor is identified by someone visiting your website from a browser that is not previously known to the tracking platform used to measure visitors. Most tools use cookies to identify unique visitors, and as such, will count the same visitors as multiple unique visitors if they delete their browser cookies or visit your website from a different browser or device.
Impressions
An impression is measured every time an ad is displayed to a targeted user. An impression might also refer to other situations such as the number of times your website has shown up for a keyword when looking in a Google Search Console report.
CPC: Cost Per Click
Cost per click is the amount of money spent on a single click on a digital advertisement. It is one of the most commonly reported metrics for any advertising platform.
PPC: Pay Per Click
Pay per click is a bidding model available in advertising systems such as Google Ads and Facebook Ads. Every time the advertising platform sends a visitor to your website from a click on your ad you pay an amount. This bidding model also ensures that you won’t pay for ads if you don’t get any clicks to your website from them.
CPA: Cost Per Acquisition
Cost per acquisition is the cost you pay per customer you acquire through an ad. In most cases, this will be an e-commerce transaction but can be customized to be other important customer actions and conversions.
CPM: Cost per Mile but rather cost per 1000
CPM Is the cost you pay to an advertising platform for 1000 impressions of an ad. If your CPM is $2, that means you are paying $2 for every 1000 impressions of your ad. As with CPC, this is one of the most common metrics you can find in any advertising platform.
It’s all about that RATE, about that RATE. No trouble!
Marketing effectiveness is calculated based on different rates such as conversions, website visitors, or the return on investment. These rates can indicate and highlight the digital marketing strategies that work or those that require improvement or optimization. Digital marketing is not an exact science, but rather a series of experiments or A/B tests which in the end will show you what type of activities can help your business grow. In order to identify the good strategies you have to take a look at data and results such as the ones below:
Conversion or Goal
A conversion or goal is an important action you want visitors to perform. Examples include ecommerce
purchases, form submissions, phone calls, and video views.
CRO: Conversion Rate Optimization or simply Conversion Optimization
Conversion Rate Optimization is the process of increasing the percentage of visitors who complete your goals. One strategy is reviewing your sales channel and finding ways to improve the process, which could be fewer clicks for the customer to reach the purchase stage, or offer a discount if they abandon the cart. A conversion doesn’t only refer to sales but can be other conversions before the purchase point, such as subscribing to a newsletter, taking a free trial, or submitting a contact form.
A/B testing is one of the most effective ways to improve conversion rates — by experimenting with content, layouts, or CTAs and seeing what actually works with your users.
👉 Want to dive deeper? Read our complete guide to A/B testing to learn how to set up, run, and scale experiments that move the needle — all from right inside Umbraco Engage.
CTR: Click-Through Rate
The click-through rate is the number of times people click on an item of interest, like an advert, in comparison to the number of times users are exposed to that item.
The calculation: Clicks divided by Impressions.
BR: Bounce Rate
A bounce is a single interaction session on your site, meaning that if someone landed on your website and didn’t do any other interaction event, like going to another page, before exiting is considered a bounce. A high bounce rate might indicate that the visitor didn’t find what they were looking for and quickly exited. This might be an indication of a bad user experience.
The calculation: Single interaction sessions divided by Total sessions
CR: Conversion Rate
The conversion rate is the ratio of conversions to visits. It is often used to measure digital performance and is a key metric for most online businesses.
The calculation: Conversions divided by Pageviews/Sessions/Users (depending on the context)
ROI- return on investment
Return on investment is a more generic term that is applicable to all businesses that focus on generating profits. It’s a ratio calculated by dividing the return on investment/net investment. Basically, see how many times you get back the money you have invested in order to assess if you’ve made a good investment.
In a digital marketing context, an example can be: say you’ve run a campaign for your company on Facebook. With the help of cookies, you can track the source of the customers. You are selling a skincare device. The skincare device costs $80. You sell 50 of them. You spend $1,100 on the ads.
You take the revenue obtained from this Facebook campaign and divide it with the ad budget you set, then multiply it by 100.
80 x 50 /1100 = 4000 / 1100 = 3,63 ROI. This all means, that for every $1 you pay you get a return of $3,63.
That’s it! The most used terms in digital marketing in one article.
If you are interested in web development acronyms you might also like this article by Umbraco.